

Tabulate positive test results in one column and negative test results in the other.įor data from prospective and experimental studies, the top row usually represents exposure to a risk factor or treatment, and the bottom row is for controls. One sample has the disease or condition you are testing for, the other does not. Contingency tables also assess the accuracy of a diagnostic test.The rows represent alternative treatments, and the columns tabulate alternative outcomes. Contingency tables can also tabulate the results of some basic science experiments. Enter the number with leukemia in one column, and the number without leukemia in the other column. After a suitable period of time, assess whether each animal has leukemia. Half are exposed to EMF, while half are not.
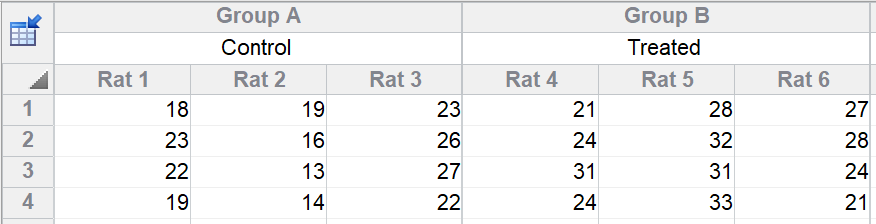
For example, you could perform a study of the EMF/leukemia link with animals. The outcomes are tabulated in the columns.
Half get one treatment, half the other (or none). In an experiment, you manipulate variables.This design is also called a case-control study. Enter the number with low exposure in one row, and the number with high exposure in the other row. Then you would assess EMF exposure in all subjects. To perform a retrospective study of the EMF-leukemia link, you would recruit one group of subjects with leukemia and a control group that does not have leukemia but is otherwise similar. A retrospective case-control study starts with the condition being studied and looks backwards at potential causes.Subjects that get leukemia are tabulated in one column the rest are tabulated in the other column. Then you would follow all subjects over time and tabulate the numbers that get leukemia. These two groups define the two rows in the table.

To perform a prospective study of the EMF-leukemia link, you would select one group of subjects with low exposure to EMF and another group with high exposure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
